Stunning Tips About What Is ADC And RDC
ADC and RDC
1. What are ADC and RDC in the data center world?
Ever feel like you're swimming in acronyms when talking about technology? You're not alone! Today, we're diving into two important ones in the world of data centers: ADC and RDC. Think of them as key pieces in the puzzle of how information travels and gets stored. Let's break it down in a way that even your grandma could understand — well, maybe. Okay, probably not your grandma, but hopefully, you'll get it!
ADC stands for Application Delivery Controller. Now, that sounds fancy, right? Basically, it's like a traffic cop for your applications. Imagine a busy highway with cars (data) trying to get to different destinations (servers). The ADC manages that traffic, ensuring everything flows smoothly, efficiently, and securely. It makes sure users get the best possible experience when using applications, whether it's streaming your favorite cat videos or making an online purchase. If an app is slow, blame the ADC! (Just kidding... mostly.)And then we have RDC, which stands for Regional Data Center. Think of it as a data center strategically located in a specific geographic region. These centers are crucial for reducing latency — that annoying delay you experience when loading a website or playing an online game. By having data stored closer to the users who need it, RDCs ensure faster access and a better overall experience. It's all about bringing the data closer to home... or at least closer to your computer!
So, to recap, ADC is the traffic manager for applications, optimizing performance and security, while RDC is a strategically placed data center designed to minimize latency and improve access speeds. They both play vital roles in ensuring that our digital lives run smoothly, even if we don't realize they're there. They're like the unsung heroes of the internet.

More Than Toxins—Current Prospects In Designing The Next Generation Of
Application Delivery Controller (ADC) Explained
2. Diving deeper into ADC functionalities
Okay, so we know ADC is the application traffic cop, but what does that actually mean? It's not just standing there blowing a whistle! These controllers perform several crucial functions. They load balance, meaning they distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent any single server from getting overloaded. This is vital for handling peak demand, like when everyone's trying to buy concert tickets at the same time. Without load balancing, the whole system could crash and burn!
Another key feature of ADCs is application security. They act as a first line of defense against malicious attacks, like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which attempt to overwhelm a server with traffic. The ADC can identify and block these attacks, protecting the applications and data from harm. Think of it as a digital bodyguard, always on the lookout for trouble. And if they see some trouble coming? BAM, they get rid of it.
Beyond security and load balancing, ADCs also optimize application performance through caching and compression. Caching stores frequently accessed data closer to the user, reducing the need to fetch it from the server every time. Compression reduces the size of the data being transmitted, which further improves speed. It's all about making things faster and more efficient, so you can get back to binge-watching your favorite shows without interruption. (We all do it.)
In essence, the ADC is a multi-tasking wizard, ensuring that applications are fast, secure, and reliable. It's the behind-the-scenes technology that makes our digital lives run smoothly, even when things get chaotic. So next time your app is working flawlessly, give a little thanks to the often-overlooked ADC!

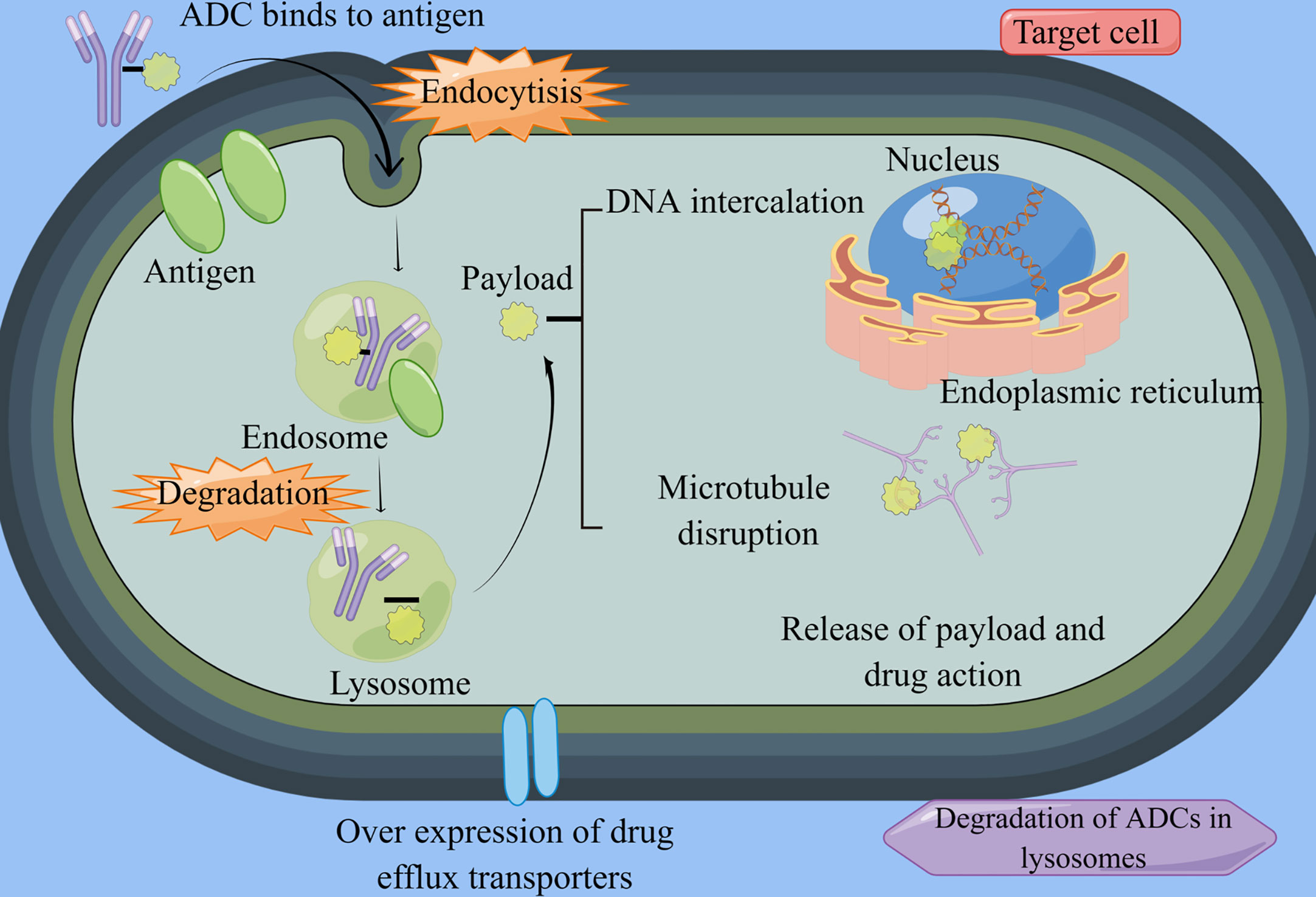
9 Types Of Drug Conjugates Overview ADC、RDC、ISAC、SMDC、AOC.pdf
Regional Data Center (RDC) in Detail
3. The strategic advantage of RDCs
We've established that an RDC is a data center located strategically within a region, but why is that such a big deal? Well, as we hinted at earlier, it's all about latency. The further data has to travel, the longer it takes to get to you. It's like ordering pizza — the closer the pizzeria, the faster you get your food. The same principle applies to data centers.
By placing data centers closer to users in different regions, RDCs minimize the distance that data has to travel, resulting in lower latency and faster response times. This is especially crucial for applications that require real-time interaction, such as online gaming, video conferencing, and financial trading. Imagine trying to play a first-person shooter with high latency — you'd be dead before you even knew what hit you!
But RDCs offer more than just lower latency. They also improve reliability and redundancy. By distributing data across multiple locations, organizations can ensure that their data is always available, even if one data center experiences an outage. It's like having a backup plan in case of disaster. You never know when something might go wrong, so it's always good to be prepared.
Furthermore, RDCs can help organizations comply with local data privacy regulations. Many countries have laws that require data to be stored within their borders. By having RDCs in those countries, organizations can ensure that they are complying with these regulations. It's about respecting local laws and ensuring that data is handled responsibly.
ADC vs. RDC
4. Comparing and contrasting ADC and RDC
So, we've covered ADC and RDC separately, but how do they stack up against each other? And more importantly, how do they work together? The main difference is their focus. ADC focuses on optimizing application delivery within a data center or across multiple data centers. It's about making applications fast, secure, and reliable. Think application-centric. On the other hand, RDC focuses on the physical location of data centers and minimizing latency for users in specific regions. Think location-centric.
However, they're not mutually exclusive. In fact, they often work hand-in-hand to deliver a seamless user experience. For example, an ADC might be deployed in an RDC to optimize the delivery of applications to users in that region. The ADC ensures that the applications are running efficiently, while the RDC ensures that the data is close to the users. It's a perfect synergy.
Think of it like this: the RDC provides the foundation — the physical infrastructure and proximity to users — while the ADC fine-tunes the application delivery process, ensuring that everything runs smoothly and efficiently. Together, they create a powerful combination that can significantly improve the performance and reliability of applications.
Ultimately, both ADC and RDC are essential components of a modern IT infrastructure. They play different roles, but they both contribute to delivering a better user experience. Understanding the differences and synergies between them is crucial for building a robust and efficient data center architecture.

The Future of ADC and RDC
5. Trends and predictions for ADC and RDC
The world of technology is constantly evolving, and ADC and RDC are no exception. So, what does the future hold for these critical components of data center infrastructure? One major trend is the increasing adoption of cloud-based ADCs and RDCs. Cloud-based solutions offer greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premises solutions. They allow organizations to easily scale their resources up or down as needed, without having to invest in expensive hardware.
Another trend is the growing importance of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in managing ADCs and RDCs. Automation can help to streamline tasks such as load balancing, security monitoring, and performance optimization. AI can be used to predict potential problems and proactively address them before they impact users. Imagine an ADC that can automatically detect and mitigate DDoS attacks before they even reach the server. That's the power of AI.
Furthermore, we can expect to see continued innovation in ADC and RDC technologies, driven by the increasing demands of modern applications. As applications become more complex and data-intensive, ADCs and RDCs will need to evolve to meet these challenges. This could include new features such as support for emerging protocols, enhanced security capabilities, and more advanced optimization algorithms.
In conclusion, the future of ADC and RDC is bright. These technologies will continue to play a vital role in delivering a seamless and reliable user experience, even as the demands of modern applications continue to evolve. By embracing cloud-based solutions, automation, and AI, organizations can unlock the full potential of ADCs and RDCs and stay ahead of the curve.

FAQ about ADC and RDC
6. What are the main benefits of using an ADC?
The main benefits include improved application performance, enhanced security, increased reliability, and better scalability. It's like giving your applications a super boost!
7. How does an RDC help with latency?
By locating data centers closer to users, RDCs minimize the distance data has to travel, resulting in lower latency and faster response times. Think of it as a short-cut for your data.
8. Can a small business benefit from using an ADC or RDC?
Absolutely! While they're often associated with large enterprises, even small businesses can benefit from the improved performance, security, and reliability that ADCs and RDCs offer, especially if they have a geographically dispersed customer base or rely heavily on online applications.