Outstanding Info About CAN H Vs L
CAN H vs. CAN L
1. Understanding the Basics of CAN Bus
Ever wondered how all the different parts of your car "talk" to each other? It's not like they're using tiny walkie-talkies (although that would be pretty cool). Instead, they use something called a CAN bus, which stands for Controller Area Network. Think of it as the car's central nervous system, allowing everything from the engine control unit (ECU) to the anti-lock braking system (ABS) to communicate effectively. Its all about sharing data, so your car can respond accordingly.
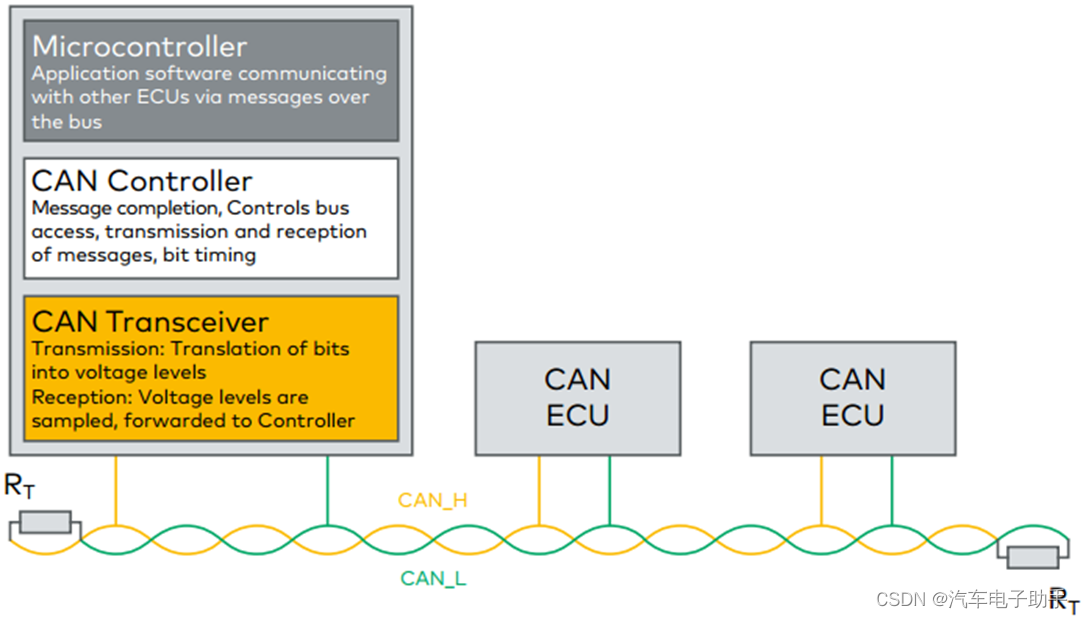
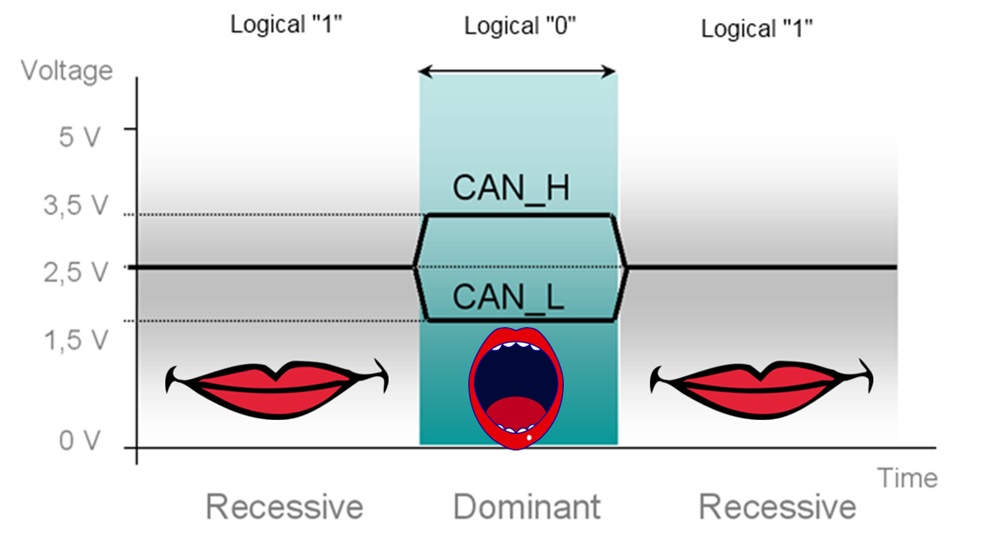
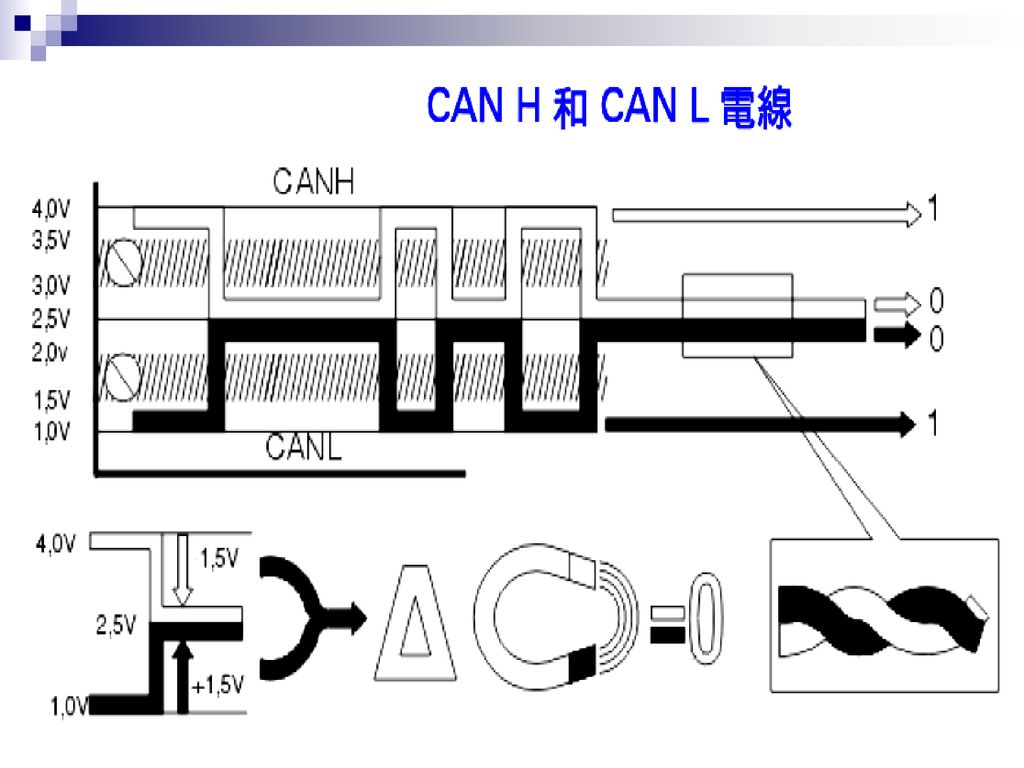
The CAN bus relies on two wires, usually referred to as CAN High (CAN H) and CAN Low (CAN L). These aren't just random names; they represent the two voltage levels used to transmit data. It's like Morse code, but instead of dots and dashes, we have high and low voltage signals. The clever part is how the difference in voltage between CAN H and CAN L determines whether a "dominant" (0) or "recessive" (1) bit is being sent. Its all about that voltage differential.
Without this communication network, your car would be a chaotic mess of independent systems. Imagine trying to parallel park if your steering wheel and brakes weren't communicating! The CAN bus ensures everything works harmoniously, making modern vehicles safer and more efficient. So next time you're cruising down the road, remember the unsung hero beneath the hood: the CAN bus.
So, how do CAN H and CAN L actually work together? Well, one line doesn't simply go up when the other goes down. Instead, they operate in tandem to create a differential signal. This is key for noise immunity and error detection, something crucial in the electrically noisy environment of a car. Think of it as a sophisticated game of see-saw where both sides are constantly moving but the difference in their position is what matters. If one side is significantly different than the other, the car's computer can detect an error and take action to prevent problems. Consider it a form of built-in error correction, ensuring reliability.
2. CAN H
CAN High (CAN H) is one half of the dynamic duo, the one responsible for the higher voltage level during data transmission. Typically, the resting voltage of CAN H is around 2.5 volts, but when a dominant bit (a "0") is sent, the voltage increases. This increase, relative to CAN L, is what signifies a specific message or instruction. It is the brighter side of the duo.
Think of CAN H as the assertive partner in the communication process. When it needs to get a message across, it raises its voltage level to make sure it's heard. It's the signal that's "pushing" the data out onto the network. In contrast to CAN L, CAN H does the heavy lifting on the voltage side of the equation.
It's essential that CAN H functions properly because any issues can disrupt the entire communication network. A faulty CAN H line can lead to all sorts of weird problems, from warning lights on the dashboard to complete system failure. Therefore, keeping an eye on the CAN H signal during diagnosis is important for a mechanic.
Proper maintenance of CAN H is crucial. Any breaks, shorts, or corrosion in the wiring can seriously affect its performance. Regular checks and ensuring proper connections are necessary to keep your car's communication flowing smoothly. A little preventive care can go a long way in avoiding potential headaches. Think of it as ensuring a clear and uninterrupted flow of information.
3. CAN L
Now, let's turn our attention to CAN Low (CAN L). While CAN H is busy raising the voltage, CAN L is there to provide the other half of the differential signal. Like CAN H, CAN L usually sits at a resting voltage of around 2.5 volts. But when a dominant bit is sent, CAN L's voltage decreases. This coordinated dance between CAN H and CAN L is what allows the car's computer to interpret the data being transmitted. In short, CAN L is the foundation for CAN H's high voltage signaling.
You could think of CAN L as the grounding force, the partner that ensures stability and accuracy. While CAN H is pushing the signal upwards, CAN L is pulling it downwards, creating a clear and reliable differential. It's the foundation that makes the entire system reliable. It is less flashy but every bit as important.
Just like CAN H, CAN L needs to be in tip-top shape to ensure smooth communication. Problems with the CAN L line can cause issues that mirror those of CAN H problems, such as erratic sensor readings and malfunctioning systems. This makes its consistent performance paramount.
Proper grounding and secure connections are vital for CAN L. Make sure the wiring isn't damaged or corroded. After all, a weak link in the CAN L can disrupt the whole communication chain. Think of it as ensuring a solid and unwavering foundation for the entire system.
4. Why the Difference Matters
So, what's the big deal about having both CAN H and CAN L? It all boils down to something called differential signaling. Instead of relying on a single wire to transmit data, the CAN bus uses the difference in voltage between CAN H and CAN L. This offers some significant advantages.
First, differential signaling is incredibly resistant to noise. Because the signal is based on the voltage difference, any noise that affects both CAN H and CAN L equally (common-mode noise) is effectively canceled out. Imagine listening to music in a noisy room — it's easier to hear the music if it's coming from two speakers playing slightly different sounds rather than one speaker battling the noise alone.
Second, differential signaling improves error detection. The CAN bus can constantly monitor the voltage difference between CAN H and CAN L. If the difference falls outside a certain range, the system knows something's wrong and can take corrective action. This robust error detection is crucial for ensuring the reliability of safety-critical systems like ABS and airbags.
Finally, differential signaling allows for higher data transmission rates. By using the voltage difference, the CAN bus can transmit data faster and more accurately than a single-ended system. This is essential in modern vehicles, which rely on a constant stream of data to operate efficiently and safely. In essence, the combination creates an efficient and safe form of data transfer.
5. Troubleshooting CAN H and CAN L Issues
If your car's CAN bus is acting up, figuring out if the problem lies with CAN H or CAN L (or both!) is the first step. Here are a few things to look for:
First, use a multimeter or oscilloscope to check the voltage levels on both CAN H and CAN L. A healthy CAN bus should have a resting voltage of around 2.5 volts on both lines, with changes in voltage during data transmission. Deviations from these values can indicate a problem. An OBD2 scanner can provide error codes that point you in the right direction, giving you hints as to where to begin your investigation.
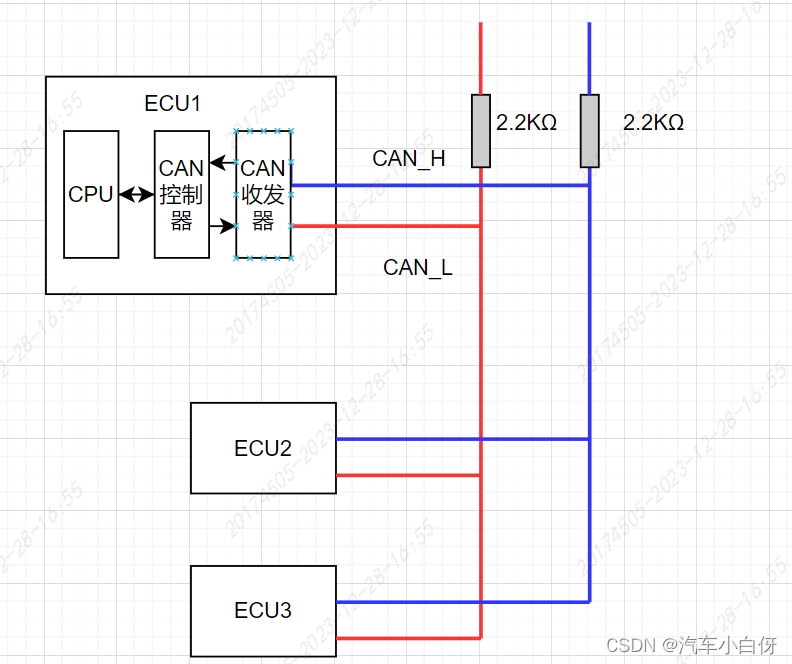
Second, inspect the wiring for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Pay close attention to the connectors and grounding points. Also, make sure the CAN bus terminator resistors are in good condition. A damaged terminator resistor can lead to signal reflections and communication errors. A break in either wire is a potential source of major problems.
Finally, consider the symptoms your car is exhibiting. Are there multiple warning lights on the dashboard? Are certain systems malfunctioning or not responding? These clues can help narrow down the possible causes and guide your troubleshooting efforts. By thinking holistically, you increase your odds of finding a solution quickly. Often multiple symptoms mean a more wide-spread issue with the CAN network as a whole.

Learn, Lean, Leer American English Pronunciation